Introduction
Root cause analysis (RCA) is a process which is implemented and used by health professionals to learn how and why errors occurred. Millions of patients are harmed in the United States(US) every year in the health care they provide (Agency for health care research and Quality (2014).This harm can result in death or injury to the patients costing the hospital millions of dollars in damages to the family and for the healthcare provider facing the RCA process which may or may not lead to termination of their position at their organization.
All health care providers and organization responds to some events where patient harm has occurred by investigation the event in question with the intent of eliminating the possibility or reducing the likelihood of a future similar event. Some organization have robust RCA process and have made huge strides toward improving patient safety, including sharing lessons widely so that others can learn from their experience (Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (2008).
In this paper, the writer will RCA process and identify three (3) system failures that occurred. Compare & contrast these failures to current processes & practice within the writer's facility/institution. Identify a minimum of three (3) Business Intelligence (BI) tools or applications (dashboards, reporting) that can be used to minimize or prevent similar failures. They are using what the writer has learned about the technology system life cycle and the use of technology to improve patient safety and patient confidentiality and to examine the technology system life cycle joint application with Donabedian’s quality framework to influence data-driven process improvement in the writers clinical setting.
Describes system failures with literature support
In Texas, Christus Spohn Hospital South in Corpus Christi, there was a hospital medication error. There were 14 premature babies given the wrong heparin dose of mediation. Instead of getting a pediatric dose to flush their, lines, an adult dose of heparin was administered to the babies. There were a few system failures that contributed to mediation errors 1). The neonates were prescribed much higher concentrations of blood thinners due to a pharmacy dosing error. 2). The neonates overdosed on heparin as a result of a registered nurses (RN) mistake.3) the hospital used adult dosage vials of Baxter heparin instead of pediatric dosage vials.
When a mistake is identified that involves patient harm there needs to be a process in paced that promptly access if actions are required ti mitigated the risk to the patient even before the formal RCA process is underway. Immediate actions may include taking care of the patient disclosure, making the situation safe, notifying police or security if appropriate, preserving evidence and gathering relevant information to understand the situation. With regards to the overdose of heparin, there should be immediate actions, taking care of neonates and their families, making the situation for others, and sequestering equipment, products devise that was involved and should happen within 72 hours of the occurrence of the event, it should be scored using the facilities approved the risk-based prioritization system. The pharmacist should be more vigilant in checking the medication before sending it to the floor. The pharmacist must be double-checking the medication and scanning it to a mediation system to reduce medication errors.
The RCA is required, to review needs that needs to be initiated, as soon as possible following the event in order to capture details while there is still fresh in the minds of the RN and pharmacy tech and pharmacist that did not check the correct does of heparin prior. At the organization that the writer's works for starting the event review promptly can be achieved if steps have been taken ahead of time to ensure staff and resources will be available. They will be scheduling of RCA team meeting each week, or will be canceled if not needed. It is important to remember that the team is convened to discover what happened, why it happened, and what can be done to prevent it from happening again. At the writer organization, the RCA process does not last longer than 45 days.
The writer works at Southern Ocean Medical Centre(SOMC) in the emergency department (ED) as the assistant nurse manager. Last year the ED went through an RCA process. A patient presented himself to the ED with depression and thoughts of killing himself. While the RN was triaging him, he had a seizure in triage. The RN called for help; the patient was stabilized and immediately brought back to a room. The RN completed the triage; however, did not communicate with the receiving RN that the patient was suicidal; hence, no suicidal precautions were implemented for this patient. When the RN when to access the patient, he noted that the patient had the cardiac monitor wires around his neck, he immediately took action and cut the wires. The RN immediately placed the patient on suicide precaution; all the equipment from the room was removed, and the patient was placed on a 1:1 observation. The nurse manager was informed who then informed the department of outcomes. This case went through the RCA review process.
Several meetings were held to complete the RCA process. The meetings were 1.5- 2 hr. in length for the interview process. The nurse manager and supervisor served as the leaders on the RCA process. Once the RCA were done, the department of the outcome made a recommendation so that this event does not happen again. The outcome of the RCA was to improve handoff communication, listening to the keys words of the triage process when the patient is communicating. Make sure that the triage RN is completing the suicide risk upon triage. This case was reportable; the Department of Health was notified.DOH visited SOMC. The ED had to do audit 30 charts to see if the RN is completing the suicide risk assessment upon tirage. The RNs had to educate the rest of the team members on suicide precautions.
There are few examples of outcomes for patient safety, and the ability to perform root cause analyses and healthcare failure mode effects analyses, and the ability to generate effective safety communications using structured formats such as the Situation-Background-Assessment (Kohn et al. 2000). Recommendation (SBAR) situational briefing model. SBAR is widely used in patient safety work, and competence in their use is essential for a healthcare professional to practice safely.
Identifies three BI tools or applications to reduce the risk of similar failures
Avoiding patient harm is vital to the work of healthcare professionals. Business Intelligence (BI) comprises an integrated system of IT tools that allow healthcare professionals to transform data into informed actions (Golfarelli, 2004). The Institute of Medicine (IOM) report on preventing medication errors recommends that healthcare systems capture electronic information on safety and use the data to improve the quality of their care delivery systems ( Institute of Medicine,2001).
Data warehouses and BI technologies have been used in healthcare settings to improve workflow efficiency, monitor quality and improve outcomes, develop best practices, optimize insurance procedures, and uncover patterns of increased expenditures (Borlawsky,2008). Many health systems are also using ‘scorecard’ and ‘dashboard’ methodologies and developing Web-based query and reporting tools to optimize the delivery of services as well as improve their data
While many health systems have achieved the former, translating burgeoning data stores into meaningful safety improvement initiatives has proven difficult. Careful deployment of health analytics tools can allow health systems, hospitals, and individual clinical staff to maximize the value of clinical and administrative data, in many cases without extensive investment in additional HIT infrastructure. By adapting proven information management strategies, patient safety and outcomes can be improved, and public health efforts can be more effectively supported (Loshini, 2003).
Applies Donabedian’s cycle of the structure, process, and outcomes to improving safety and confidentiality in a clinical setting
Clinicians, nurses, and managers in hospitals are continuously faced with new technologies and methods that require changes to be made to the working environment. Quality systems help to manage changes while maintaining a high quality of care. A new model of quality systems which was inspired by the works of Donabedian has three factors which are a structure (resources and administration), process (culture and professional co-operation), and outcome (competence development and goal achievement). Donabedian's model to analyze quality includes three factors: structure, process, and outcome. Structure refers to prerequisites, such as hospital buildings, staff, and equipment. Process describes how the structure is put into practice, such as specific therapies. Outcome refers to results of methods, for instance, effects of treatment (Donabedian, 1980).
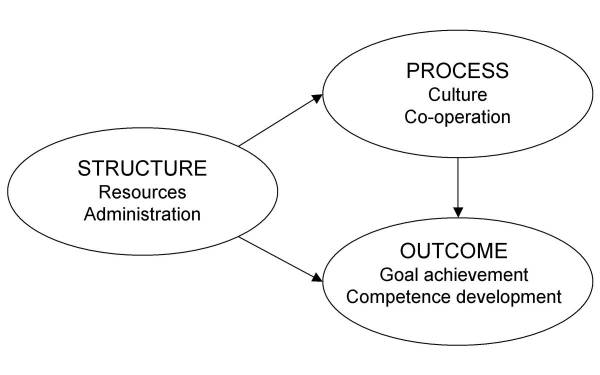
Figure 1 Donabedian Model
Donabedian has suggested that structure, process, and the outcome may be related but that such relationships could be challenging to show. The Donebedian Model, the review process can be done effectively and giving feedback to the patients and or family and team members in the organization
Conclusion
The key to establishing a successful RCA analysis and action process lies in leadership support. The piece of a successful program includes establishing a transparent risk-based method for triaging events, selecting the correct personnel to serve on the team, providing the team with the resources and time to complete the review and measuring the actions to assess if they are were effective in mitigating the risk.
References
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (2014).Efforts to improve Patient Safety Results in 1.3 Million Fewer Patient Harms. AHRQ Publication 15-0011
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (2008). Patient Safety Organisation (PSO) Program.
- Borlawsky., T, LaFountain J, Petty., L, (2008). Leveraging an existing data warehouse to annotate workflow models for operations research and optimization. AMIA Annu Symp Proc.November 6:885.
- Donabedian A (1980).Explorations in Quality Assessment and Monitoring (1980). Volume I. The Definition of Quality and Approaches to its Assessment. Ann Arbour, MI, Health Administration Press pp. 1–164.
- Golfarelli., M, Rizzi., S, Cella., I. Beyond data warehousing: what is next in businessintelligence? Proceedings of the 7th ACM international workshop on Data warehousing and OLAP. Washington, DC, USA: ACM, 2004:1–6
- Institute of Medicine, Chapter 7 (2001). Using information technology. In: Crossing the quality chasm: a new health system for the 21st century. Washington, DC: National Academy Press
- Loshin., D (2003). Business intelligence: getting onboard with emerging IT. San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers
- Resetar., E, Noirot. L.A, Reichley., R.M (2007).sing business intelligence to monitor clinical quality metrics. AMIA Annu Symp Proc 1092.
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below:

